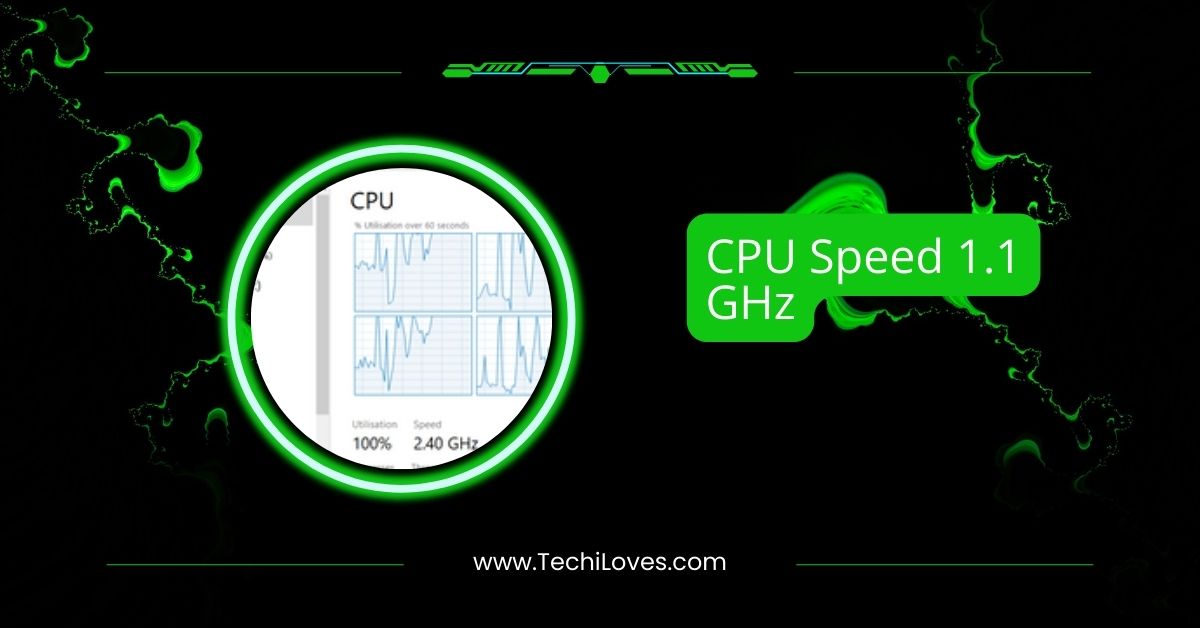
When choosing the right processor for your computer, understanding CPU speeds like 1.1 GHz is essential.
A 1.1 GHz CPU processes 1.1 billion cycles per second. While it’s slower than a 2.4 GHz processor, it’s suitable for everyday tasks like browsing and schoolwork. For gaming or demanding apps, higher speeds are recommended.
In this article, we’ll dive into what 1.1 GHz CPUs are, their advantages and limitations, and how you can make the most out of your processor, whether you’re working, gaming, or just browsing the web.
Understanding GHz
GHz stands for gigahertz, a unit that measures how fast a processor works. One GHz equals one billion cycles per second. A higher GHz means a faster CPU, helping the computer run tasks quicker and more efficiently.
CPU Speed: 1.1 GHz Explained
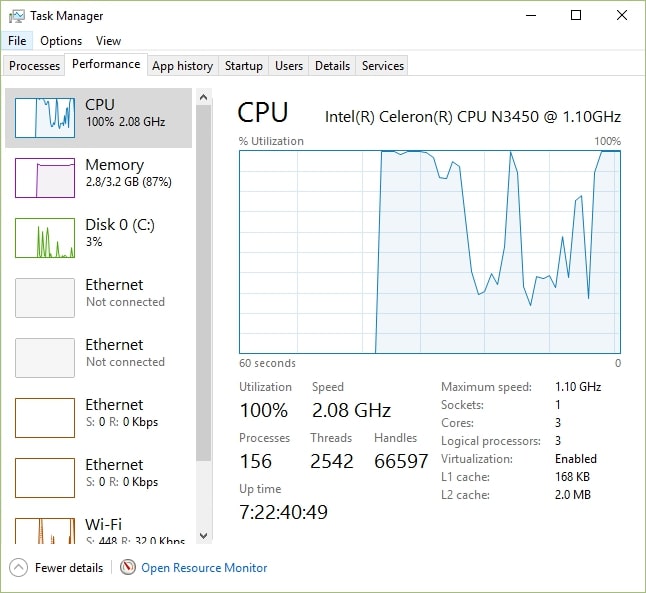
A 1.1 GHz CPU completes 1.1 billion cycles every second. While it’s not the fastest speed, it’s good enough for everyday tasks like browsing and word processing. It may struggle with more complex activities like gaming or video editing.
What Does CPU Speed Mean?
CPU speed, measured in GHz (gigahertz), tells how fast a processor can work. It counts the number of tasks a CPU can handle in one second. Higher speed means better performance, but factors like cores and design also matter.
Where Are 1.1 GHz CPUs Used?
1. Entry-Level Laptops and Chromebooks
These devices use 1.1 GHz CPUs for simple browsing, typing, or streaming tasks. They are affordable and perfect for students or casual users who don’t need heavy processing power.
2. Tablets and Smartphones
Many budget tablets and smartphones have 1.1 GHz CPUs. They handle everyday apps, calls, and media smoothly while saving battery life, making them ideal for light users.
3. IoT Devices and Embedded Systems
IoT devices, like smart home gadgets, often use 1.1 GHz CPUs. They perform specific tasks efficiently without needing high power, making them reliable for automation and connectivity.
4. Single-Board Computers
Single-board computers like Raspberry Pi use 1.1 GHz CPUs for learning, coding, and small projects. They are compact, affordable, and great for beginners or DIY enthusiasts.
Also Read: Not Enough CPU For Conversion Of This Item – Quick Fixes!
Advantages of 1.1 GHz CPUs
- Energy Efficiency: These CPUs consume less power, making them ideal for laptops and tablets, which helps extend battery life.
- Affordable: 1.1 GHz processors are usually less expensive, making them budget-friendly for users needing basic performance.
- Low Heat Generation: They produce less heat, reducing the need for advanced cooling systems and ensuring a quieter operation.
- Good for Basic Tasks: Perfect for everyday activities like web browsing, document editing, and streaming without slowing down.
- Quiet Operation: These CPUs run more quietly with lower processing speeds, offering a peaceful user experience.
Limitations of 1.1 GHz CPUs
- Limited Performance for Heavy Tasks: 1.1 GHz CPUs struggle with resource-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering.
- Not Ideal for Multitasking: Handling multiple applications simultaneously can cause lag and reduced system responsiveness.
- Inadequate for Future Software: As software becomes more demanding, a 1.1 GHz CPU may struggle to keep up.
- Lower Benchmark Scores: These processors score lower in performance tests than higher-speed CPUs, limiting their appeal to tech enthusiasts.
- Potential Compatibility Issues: Some modern software may not run efficiently on a 1.1 GHz CPU, limiting usability for users who need the latest applications.
Tips for Optimizing Performance on 1.1 GHz CPUs
- Close Unnecessary Background Applications: Shut down unused programs to free up CPU resources, improving overall performance.
- Upgrade RAM: Adding more RAM can boost multitasking capabilities and overall system responsiveness.
- Use Lightweight Software: Opt for apps and browsers designed for lower-spec systems to avoid CPU overloading.
- Regularly Clean Your System: Run antivirus and cleanup tools to remove malware and junk files, maintaining smooth performance.
- Adjust Power Settings: Set your computer to “High Performance” mode to ensure your CPU runs at its best when needed.
The Role of CPU Architecture
CPU architecture is the design that makes a processor work. A modern 1.1 GHz CPU with advanced architecture can perform better than an older one because it handles tasks more efficiently, even at the same speed.
What Is a PC Processor And What Does it Do?
A PC processor, also called the CPU, is the brain of your computer. It processes instructions, runs programs, and performs calculations. The faster it works, the better your computer can handle tasks smoothly.
Processor Cores Versus Clock Speed
1. What is a processor core?
A processor core is part of the CPU that handles tasks. More cores allow the CPU to manage multiple tasks simultaneously, improving performance.
2. What is clock speed?
Clock speed is how fast a CPU can process instructions. It’s measured in GHz, with higher speeds meaning faster performance and better multitasking ability.
3. How do I choose between more processor cores or a higher clock speed?
Choose more cores for multitasking and heavy apps. Higher clock speed is better for tasks that need fast processing, like gaming or video editing.
4. What is a good processor speed for a laptop versus desktop?
Laptops need around 2.0 GHz for everyday tasks. Desktops often have speeds above 2.5 GHz, focusing more on performance for demanding tasks.
What is Processor Speed?
Processor speed refers to how quickly a CPU can execute tasks. It’s measured in GHz, with higher speeds typically meaning faster performance for applications and programs, improving overall system responsiveness.
What Makes a Good CPU Speed?
A good CPU speed depends on your tasks. For general use, 2.0 GHz is fine. Aim for 3.0 GHz or higher for gaming or professional functions for smoother performance and better multitasking.
Must Read: CPU Privileged Time Is Too High Zabbix – Important Guide!
Processor Speed for Laptops vs Desktops
1. What is a Good Processor Speed for a Laptop?
For everyday tasks like browsing and office work, 1.5-2.5 GHz is ideal. For more demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, aim for 3.0 GHz or more for better performance.
2. Desktop CPU Speeds
Desktop CPUs usually have speeds of 3.0 GHz and above. They can handle more powerful tasks like gaming, content creation, and multitasking without draining battery life, offering top-notch performance.
Beyond Clock Speed: Other Factors to Consider
1. Number of Cores and Clock Speed
More cores allow for better multitasking and performance with demanding applications. Clock speed affects how fast tasks are processed. A balance of both is ideal for optimal performance in various tasks.
2. Multi-Core Processor
A multi-core processor has two or more cores that can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, improving multitasking and efficiency. It’s essential for running heavy applications like video editing software and gaming.
3. Multiple Cores
Multiple cores allow the processor to perform several tasks at once. This is useful for multitasking and running resource-heavy applications, improving overall performance without overwhelming the CPU.
4. Processor Cores
Processor cores are individual units within the CPU that execute tasks. More cores mean the CPU can handle more tasks simultaneously, improving performance, especially in multi-threaded programs like games or video editing.
CPU Speed 1.1 GHz Windows 11
A 1.1 GHz CPU can run Windows 11 for basic browsing or office work tasks. However, it may struggle with heavier apps or multitasking. Windows 11 works better with faster processors for smoother performance.
Is a 1.1 GHz CPU Still Relevant in 2025?
In 2025, a 1.1 GHz CPU will still work for simple tasks like web browsing or lightweight apps. However, gaming, editing, or advanced software may feel slow compared to newer, faster processors.
How Fast Can a Computer Process Information?
The speed at which a computer processes information depends on factors like CPU clock speed, number of cores, and the efficiency of other components. A faster CPU and more cores result in quicker processing.
Choosing the Right Processor for Your Needs
1. For Everyday Computing
For everyday tasks like browsing, email, and media, a mid-range processor (like Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3) is sufficient for smooth performance.
2. For Gaming
For gaming, look for processors with high clock speeds and multiple cores, like Intel Core i5 or i7, to handle demanding games and graphics smoothly.
3. For Professional Use
Opt for fast processors and multiple cores (Intel Core i7/i9 or Ryzen 7/9) for better multitasking and performance for professional use like video editing or software development.
What does processor speed really mean?
Processor speed refers to how quickly a CPU can perform tasks. It’s measured in GHz (gigahertz). A higher speed means faster processing, but other factors like cores also matter.
Is 1.1 GHz good for a laptop

A 1.1 GHz processor is okay for browsing or office work. However, it may struggle with demanding tasks like gaming or video editing.
1.10 GHz processor is good?
A 1.10 GHz processor is good for light computing tasks, like browsing or email. It’s not ideal for heavy tasks but works well for basic usage and energy efficiency.
Need To Know: Pinnacle Raven Or Summit Ridge CPU: Which One Suits You!
1.10 GHz processor meaning
A 1.10 GHz processor has a clock speed of 1.1 billion cycles per second. It indicates how fast the processor can perform calculations but doesn’t tell the full story about performance.
1.1 GHz quad-core too slow?
A 1.1 GHz quad-core processor can handle multitasking better than single-core CPUs but may be slow for demanding tasks like gaming or video editing due to its lower clock speed.
Is a 1.1 GHz Core M powerful enough for me?
A 1.1 GHz Core M processor is good for light tasks like browsing and document editing. It’s designed for efficiency, but may not be powerful enough for gaming or intensive professional work.
Intel Celeron 1.1 GHz vs 2.4 GHz
An Intel Celeron 1.1 GHz is slower than a 2.4 GHz processor but more energy-efficient. A 2.4 GHz CPU will perform better for most tasks, especially gaming or multitasking.
Is Quad Core 1.1GHz, up to 2.4GHz CPU ok?
A quad-core 1.1GHz CPU with speeds up to 2.4GHz is decent for light tasks and multitasking. It can handle basic applications, but performance might fall short for demanding programs or gaming.
The 2.5 GHz board is only reporting 1.1 GHz
If a 2.5 GHz board reports only 1.1 GHz, it could be due to power-saving features or throttling. It adjusts speed based on workload and temperature to optimize performance and energy consumption.
Is 1.1ghz Good for Gaming
A 1.1 GHz processor is not ideal for gaming. Gaming requires a faster processor, preferably 2.5 GHz or more, to handle modern games’ intensive graphics and processing demands.
CPU speed 1.1 GHz Windows 10
A 1.1 GHz CPU with Windows 10 works for basic tasks but may lag with heavier applications. For smoother performance, especially when multitasking, a faster CPU is recommended.
Is 1.1ghz processor speed good for school
A 1.1 GHz processor is sufficient for school tasks like writing papers, browsing, and research. However, it may not be fast enough for heavy multitasking or more demanding school projects.
Is 1.1 GHz good for programming
A 1.1 GHz processor can handle basic programming tasks. However, a faster processor would provide better performance for more complex programming, compiling code, or using multiple development tools.
CPU speed 1.1 GHz laptop
A 1.1 GHz laptop processor works well for everyday tasks like browsing, video streaming, and document editing. A faster processor is recommended for more intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
1.10 GHz processor generation
A 1.10 GHz processor typically belongs to an energy-efficient generation, like Intel’s low-power chips. These processors are designed for basic tasks but may not perform well in demanding applications.
Is 1.1 GHz good for Chromebook
A 1.1 GHz processor is suitable for Chromebooks and is used for web browsing, emails, and basic apps. A faster processor might be better for advanced tasks like multitasking or media editing.
Is A 1.1 GHz processor fast enough?
A 1.1 GHz processor is fast enough for light tasks like web browsing and office work. However, it can be slow for more demanding gaming or video editing applications.
What does 1.1 GHz processor mean?
A 1.1 GHz processor means the CPU can perform 1.1 billion cycles per second. It indicates the processor’s speed, but other factors, like cores, also affect performance.
Is 1.0 GHz processor speed good?
A 1.0 GHz processor is quite slow by today’s standards. It’s fine for basic tasks like web browsing and emails but struggles with heavier programs or multitasking.
Is 1.3 GHz processor speed good?
A 1.3 GHz processor offers decent performance for light tasks and casual use. A faster processor would perform better for more intensive applications, like gaming or video editing.
Read It: CPU Maximum Frequency Always 100 – Ultimate Guide – 2025!
Is 2.0 GHz good for gaming?
A 2.0 GHz processor is a good starting point for gaming, but it’s still on the lower end. Higher clock speeds and a dedicated graphics card would improve gaming performance.
What is the meaning of 1.10 GHz?
1.10 GHz refers to the clock speed of a processor, meaning it can complete 1.1 billion cycles per second. This speed impacts how quickly the CPU processes tasks.
Is A 1.6 GHz Processor Slow?
A 1.6 GHz processor is decent for everyday tasks but may struggle with demanding programs or heavy multitasking. A faster processor is better for performance-intensive applications.
Is A 1.8 GHz processor slow?
A 1.8 GHz processor is generally not considered slow. It handles basic tasks well but may fall behind when handling more resource-heavy applications like gaming or professional software.
CPU ghz stuck at base speed (1.19ghz)
If your CPU GHz is stuck at 1.19 GHz, it may be due to power-saving features or thermal throttling. Try updating drivers or checking your power settings for possible fixes.
FAQs
1. What does 1.2 GHz processor mean?
A 1.2 GHz processor runs at 1.2 billion cycles per second. It’s a mid-range speed suitable for everyday tasks.
2. Is 1GHz good for gaming?
A 1 GHz processor is too slow for gaming, as most games need faster speeds. A higher GHz is recommended.
3. Maximum speed is 1.1GHz but runs at 2.5GHz???
This means your CPU has a base speed of 1.1 GHz but can boost to 2.5 GHz when needed for demanding tasks.
4. How Fast Does Your PC Really Need to Be?
Your PC needs to be fast enough for your tasks, like browsing, gaming, or professional work. More speed helps with demanding tasks.
5. Will my laptop of 8GB RAM work fast with a processor of 1.10GHz?
Yes, your laptop should perform light tasks like browsing and watching videos well but slower for intensive programs.
6. Is an HP computer processor 1.10GHz strong enough to run a 2.0GHz program?
A 1.10 GHz processor can run a 2.0 GHz program but might struggle with more demanding tasks or multi-tasking.
7. Is 1.1 GHz actually half as slow as 2.4 GHz? Explain it to me like I’m a child.
1.1 GHz is slower than 2.4 GHz, but not exactly half. This means that the processor does fewer cycles per second.
8. How powerful is a 1 GHz processor? Is it worth buying one? If not, what processor should I buy?
A 1 GHz processor is slow for today’s tasks. For better performance, look for processors with at least 2 GHz speed.
9. Should I buy a laptop with 1.1 GHz clock speed turbo boost up to 2.4 GHz for normal usage like watching HD movies, surfing, and giving online papers?
Yes, this laptop will handle everyday tasks like browsing and watching HD movies well, with better performance on bursts.
10. The laptop I want says it has 1.1GHz of processor but with a burst speed of 2.6GHz what exactly does that mean?
The laptop runs at 1.1 GHz normally but boosts to 2.6 GHz for heavier tasks, improving performance when needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a 1.1 GHz CPU is suitable for light tasks like browsing and document editing, offering energy efficiency and affordability. However, consider a faster processor for gaming or heavy applications for better performance and smoother multitasking.